37 Orders of Insects: Mecoptera
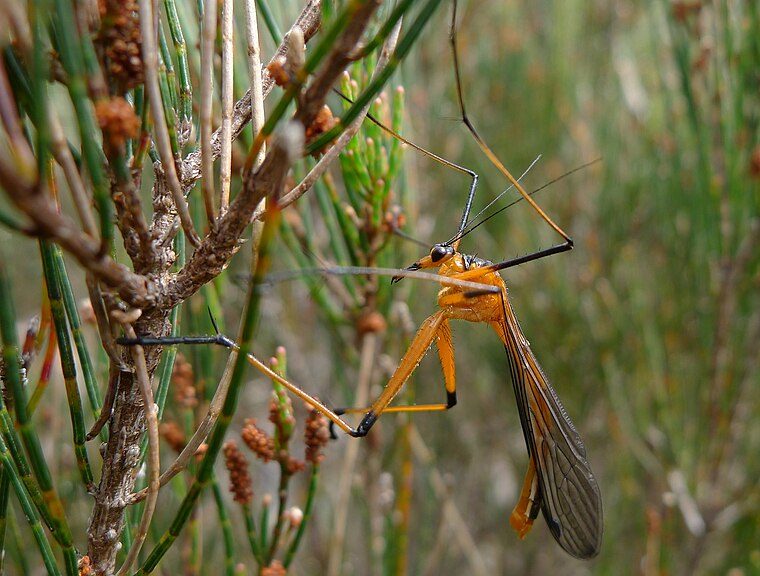

Order Mecoptera: Scorpion flies, hanging flies
Mecoptera
- common names: scorpion flies (refers to bulbous genitalia of males in the family Panorpidae curved over the abdomen–most common family–this family is not found in Australia) or hanging flies – most Australian species hang from vegetation by the fore- and sometimes the mid- legs
- from Greek: meco = long, ptera = wings; refers to long wings
- about 600 species worldwide–not common
- hanging flies are predators, preying upon small, flying insects
- larvae and adults generally omnivorous
Characteristics of Mecoptera
Adults
- small to medium sized (up to 50mm)
- elongated head with hypognathous rostrum and mandibulate mouthparts; filiform antennae
- long, narrow fore and hind wings, similar in size that extend beyond abdomen; some species wingless
- In Australian hanging flies, legs long and thin, with strong claws–catch prey with hind legs
- copulation in some species involves elaborate courtship procedures; sometimes with nuptial feeding (male provides an insect meal prior as part of courtship)
Immatures
- immature stages (larvae) mostly terrestrial,
- heavily sclerotised head capsule
- short, jointed thoracic legs
- resemble lepidopteran caterpillars but without prolegs
Topic Review
Do you know…?
- the main anatomical features of Mecoptera?

