43 ROLE AND IMPACT OF SOCIAL MEDIA IN TOURISM – Contributions by Ulrike Gretzel
In this chapter I will summarize my contributions to understanding social media. I feel passionate about my research on social media because social media have changed the way we shop/consume (Zhou, Zhang & Zimmermann, 2013), learn, play, work, explore our identities and express our creativity, socialize, date (Finkel et al., 2012), find out about new trends and world events (and the latest gadgets), support causes and create movements, entertain ourselves, do research (Kozinets, 2020), fuel and follow our passions (Kozinets, Patterson & Ashman, 2017), find support, celebrate, grieve, and build our legacies; and, of course, they have revolutionized the way we travel (Gretzel, 2018). Social media have allowed me to stay in touch with family and friends, connect with new friends and colleagues, share my interests with others and join communities I never knew existed, learn about people and places, find out about hidden travel gems, and post lots of cat pictures. My drive to capture meanings and effects of social media use therefore emerges from a deep personal need to make sense of the world around me.
Besides these impacts on individual consumers, social media have also transformed the way tourism businesses and destinations can market. Social media provide especially smaller establishments and micro-entrepreneurs around the world with new opportunities to be seen and heard and to understand and connect with potential and existing customers. Importantly, social media platforms gave rise to new technological innovations like augmented reality that are revolutionizing the information landscape for consumers and businesses alike. At the macro-level, social media have not only helped create new economies (e.g., the sharing economy or, more generally put, the reputation economy) and new forms of value (co-)creation (Vargo, Maglio, & Akaka, 2008), but they have also led to significant social and political change across the globe.
At the same time, social media have brought the worst out in people, businesses, and society. They have enabled new forms of scams and identity theft, led to misinformation, discrimination, bullying, envy, hate crimes, filter bubbles and increasing polarization, have interfered with elections, and have enabled the emergence of new tech giants and new economic dependencies as well as new forms of censorship. They continue to challenge our privacy rights, make us buy junk, chain us even more to our technological devices, and sometimes keep us from experiencing RL (real life). I have been stalked on social media, have spent way too much time scrolling through feeds, and have bought unnecessary items. And I often see and hear about the negative impacts social media can have on tourism businesses and entire communities, whether it is Airbnb contributing to housing shortages or influencers leading mobs of tourists to formerly pristine areas (Gretzel, 2019).
Both aspects of social media, the good and the bad, make it absolutely critical to understand social media as more than just technological applications. My research has tried to grasp what social media are, how they are being used by whom and for what purpose, how they facilitate but maybe also hinder certain human behaviors, how they shift power, what dependencies they create, why they are so persuasive, what promises they hold in terms of making our lives better, and how they might develop in the future. And tourism is an important application area in which to study social media as a phenomenon because it provides a context in which exploration (but also stupidity, see Pratt & Tolkach, 2020), desire, mobility, risk, social dynamics, etc. lead to unique information and sharing needs and behaviors on the consumer side, while hyper-competition, fragmentation and volatility create an industry context in which social media applications seem to particularly thrive.
Social Media – A Research Journey
My social media research journey began organically while investigating the impact of the Internet on tourism. At the time, virtual travel communities sparked my interest in travel information that was not created and promoted by traditional tourism intermediaries. However, it was not until 2006 that my interest in social media research became more focused. Two important things happened that year: 1) I was introduced to CyWorld by my Korean graduate students, who also convinced the Korean Tourism Organization to invite me to speak at the inaugural Korea e-Tourism forum about the travel stories consumers increasingly create and share online (Gretzel, Lee & Lee, 2006); and, 2) I met a group of enthusiastic people from a relatively unknown travel start-up at a conference for destination marketers in Austin, Texas who were there to convince people that their platform, TripAdvisor, would revolutionize the travel industry.
These occurrences led (besides a life-long passion for all things Korean and an addiction to social media) to formal research projects with the respective organizations and the start of a research program. The research report written for the project with TripAdvisor was the first empirical research study on online travel reviews and continues to be available on the TripAdvisor website (Gretzel, Yoo & Purifoy, 2007). Up to this point, fifteen years later, this research interest in social media has continued to keep me extremely busy because of the fast-paced and complex evolution of social media.
Social media have grown and developed in unexpected and profound ways. While my research on social media has explored many avenues and aspects connected with these technologies, there are many areas that remain virtually untouched and require examining, while others warrant re-examining. In this chapter I outline some of the streams of research to which I have contributed so far.
I wanted to depict my personal research journey in relation to social media in a somewhat systematic way to help others explore some of the topics I have been interested in. Over the years, I have written over 100 social media-related contributions that span journal articles, edited books, book chapters, conference papers, industry publications, commentaries, and even a published poem about popular hashtags. Figure 1 depicts the words that most frequently appear in the titles of these publications.

Figure 1 shows that besides addressing social media and consumer-generated media in general ways, I have done a lot of work on online reviews and have looked at impacts from consumer as well as operator and destination marketing perspectives. It also shows that I have explored social media in different geographic contexts, including China, Australia, and Iran. And, while the analysis of textual elements of social media has always been a focal area of my research, visual elements and practices (travel photos, selfies, emojis, videos, etc.) have become an ever more important part of my social media-related research interests in recent years.
Looking more broadly at these publications, my social media research addresses six different lenses through which social media can be understood. Three of these lenses pertain to the technological foundations of social media and to the informational landscape they create. The other three speak to the human side of social media and describe the social and cultural phenomena that emerge from their use (Figure 2). The six lenses or ways of understanding are, of course, highly interconnected and the diagram depicted in Figure 2 suggests that the human activity feeds back into the technological and informational infrastructure through the digital traces it creates. Thus, both technological and human perspectives are needed to grasp the complexity and dynamic nature of social media.
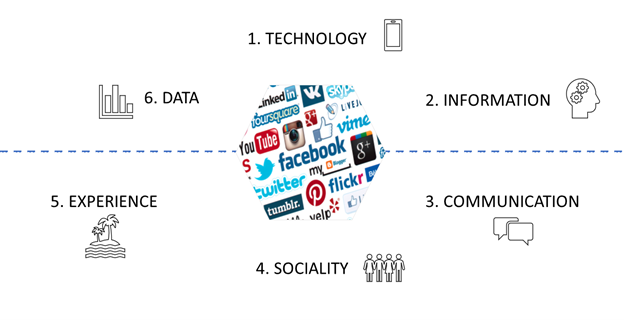
Before diving into the specific themes I explored using these lenses, I would like to note that there were a few publications that did not fit this classification. First, I have published articles, chapters and two edited books that give broad overviews of social media in tourism and therefore cover several, if not all, of these themes. They are listed in Table 1. The latest addition to this list is a co-authored review paper that examines general trends in the social media in tourism literature (Zarezadeh, Rastegar, & Gretzel, 2018). Second, I have one publication that looks at social media from a learning and teaching perspective (Isacsson & Gretzel, 2011). Unfortunately, I never pursued this specific theme further despite its obvious importance.
Table 1. General Social Media Publications.
General Social Media Publications
Sigala, M., Christou, E., & Gretzel, U. (Eds.) (2012). Social Media in Travel, Tourism and Hospitality. Brookfield, VT: Ashgate.
Gretzel, U., Sigala, M., & Christou, E. (2012). Social Media Change the Name of the Game in the Tourism and Hospitality Industries. The European Financial Review, October 20, 2012, http://www.europeanfinancialreview.com/?p=5648
Gretzel, U. & Yoo, K.-H. (2017). Social Media in Hospitality and Tourism. In S. Dixit (Ed.), Routledge Handbook of Consumer Behaviour in Hospitality and Tourism, pp. 339-346. New York: Routledge.
Zarezadeh, Z., Rastegar, R. & Gretzel, U. (2018). Reviewing the Past to Inform the Future: A Literature Review of Social Media in Tourism. Czech Journal of Tourism, 7(2), 115-131.
Sigala, M. & Gretzel, U. (Eds.) (2018). Advances in Social Media for Travel, Tourism and Hospitality: New Perspectives, Practice and Cases. New York: Routledge.
Gretzel, U. (2018). Tourism and Social Media. In Cooper, C., Gartner, W., Scott, N. & Volo, S. (Eds.). The Sage Handbook of Tourism Management, Volume 2, pp. 415-432. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.
Social Media as Technology
The first lens refers to my work on social media in tourism that seeks to understand social media as technologies. This means looking at Web 2.0 technologies as the base on which social media are built, examining specific platforms like TripAdvisor, and investigating and classifying the technological affordances that shape social media use. I have also explored the relationship between social media and other technologies (smartphones and camera-technologies like GoPros, see Dinhopl and Gretzel, 2016) to understand the wider social media and device ecosystem and its implications for tourism.
Looking at social media as technologies also involves understanding their adoption and use. I have investigated this topic from consumer and organizational perspectives. A main thread in this research stream is how adoption is shaped by national and institutional contexts. Another key topic is whether social media allowed tourism providers to “leapfrog” earlier stages of Internet technology adoption and establish their online presence solely through social media. Finally, as a persuasion scholar, I have also examined social media as persuasive technologies. Specifically, I have conceptualized the potential of social media to induce behavioral change (e.g., regarding food waste and overtourism) and to support tourism-related activism through affordances that facilitate collective action (Gretzel, 2017).
Table 2. Social Media as Technology.
Technological Foundations
Ge, J., Gretzel, U. & Clarke, R. J. (2014). Strategic Use of Social Media Affordances for Marketing: A Case Study of Chinese DMOs. In Xiang, Z. & Tussyadiah, I. (Eds.), Information and Communication Technologies in Tourism 2014, pp. 159-174. Berlin: Springer.
Gretzel, U. (2015). Web 2.0 and 3.0. In Cantoni, L. & Danowski, J. A. (Eds.). Communication and Technology, Handbooks of Communication Science (HOCS) series, pp. 181-192. Berlin: De Gruyter Mouton.
Dinhopl, A. & Gretzel, U. (2015). Changing Practices/New Technologies: Photos and Videos on Vacation. In I. Tussyadiah & A. Inversini (Eds.), Information and Communication Technologies in Tourism 2015, pp. 777-788. Berlin: Springer Verlag.
Dinhopl, A. & Gretzel, U. (2016). Conceptualizing tourist videography. Journal of Information Technology & Tourism, 15(4), 395-410.
Yoo, K.-H., Sigala, M., & Gretzel, U. (2016). Exploring TripAdvisor. In Egger, R., Gula, I., Walcher, D. (Eds.). Open Tourism: Open Innovation, Crowdsourcing and Collaborative Consumption Challenging the Tourism Industry, pp. 239-255. Berlin: Springer.
Persuasive Technology
Gretzel, U. (2017). Social Media Activism in Tourism. Journal of Hospitality and Tourism, 15(2), 1-14.
Murphy, J., Gretzel, U., Pesonen, J., Elorinne, A.-L. & Silvennoinen, K. (2018). Household Food Waste, Tourism and Social Media: A Research Agenda. In Stangl, B. & Pesonen, J. (Eds.), Information and Communication Technologies in Tourism 2018, pp. 228-239. Cham, Switzerland: Springer International.
Gretzel, U. (2019). The Role of Social Media in Creating and Addressing Overtourism. In Dodds, R. & Butler, R. (Eds.). Overtourism: Issues, realities and solutions, pp. 62-75. Berlin: De Gruyter.
Technology Adoption
Gretzel, U., Kang, M. & W. Lee (2008). Differences in Consumer-Generated Media Adoption and Use: A Cross-National Perspective. Journal of Hospitality Marketing and Management, 17(1/2): 99-120.
Shao, J. & Gretzel, U. (2012). Social media Usage by Chinese Community supported agriculture farms. CAUTHE National Conference 2012. Melbourne, VIC, February 6-9, 2012.
Gretzel, U., Kennedy-Eden, H. & Mistilis, N. (2014). Organizational Factors Driving Technology Non-Adoption in Australian Tour Operators. 21st Annual ENTER 2014 Conference. Dublin, Ireland, January 21-24, 2014. http://ertr.tamu.edu/enter-2014-volume-4-research-notes/
Gretzel, U., Mendes Filho, L., Lobianco, M., Alonso Vazquez, M. & Mistilis, N. (2017). Technology Adoption by Tourism Operators in Australia and Brazil: An Institutional Theory Perspective. ENTER 2017 Conference. Rome Italy, January 24-26, 2017. http://ertr.tamu.edu/content/issues/enter-2017-volume-8-research-notes/
Ge, J. & Gretzel, U. (2018). A new cultural revolution: Chinese consumers’ internet and social media use. In Sigala, M. & Gretzel, U. (Eds.), Advances in Social Media for Travel, Tourism and Hospitality: New Perspectives, Practice and Cases, pp. 102-118. New York: Routledge.
Zarezadeh, Z. & Gretzel, U. (2020). Iranian Heritage Sites on Social Media. Tourism Analysis, 25 (2/3), 345-357.
Soares, A. L., Mendes-Filho, L. & Gretzel, U. (2021). Technology adoption in hotels: Applying institutional theory to tourism. Tourism Review, 76(3), 669-680.
Social Media as Information
Social media platforms and applications differ from other Internet technologies because of their emphasis on the creation, sharing and curation of consumer-generated media (CGM). My research has focused on understanding the characteristics of CGM (especially their perceived trustworthiness), the motivations and traits of their creators, and their role in travel information search and decision-making processes (Table 3). Most of this research has focused on online travel reviews. My papers on false reviews were the first in tourism to investigate the phenomenon and formed the basis for later efforts by others to inform automated false review detection.
The publication that most stands out in this section is Xiang and Gretzel (2010), because it was one of the first to define social media for the tourism context and draw attention to their increasing importance and impact in the travel domain by illustrating the extent to which social media were starting to dominate travel information search. My recent work related to this theme of social media as information looks at the impact of mobile technology on consumer-generated media creation, specifically that of online travel reviews (Mariani, Borghi & Gretzel, 2019).
Table 3. Social Media as Information.
CGM Creation
Yoo, K. H. & Gretzel, U. (2008). Understanding Differences Between Online Travel Review Writers and Non-Writers. In Hara, T. (Ed.), Proceedings of the 13th Annual Graduate Education and Student Research Conference in Hospitality and Tourism, Orlando, FL, January 3-5, 2008, pp. 21-29.
Yoo, K. H. & Gretzel, U. (2009). What Motivates Consumers to Write Online Travel Reviews? Journal of Information Technology & Tourism, Special Issue on Virtual Communities, 10(4), 283-296.
Yoo, K.-H. & Gretzel, U. (2011). Influence of Personality on Travel-Related Consumer Generated Media Creation. Computers in Human Behavior, 27(2), 609-621.
Yoo, K.H., & Gretzel, U. (2012). Use and Creation of Social Media by Travelers. In Sigala, M., Christou, E., & Gretzel, U. (Eds.), Social Media in Travel, Tourism and Hospitality (pp.189-206). Brookfield, VT: Ashgate.
Mariani, M. M., Borghi, M., & Gretzel, U. (2019). Online reviews: Differences by submission device. Tourism Management, 70, 295-298.
Role in Travel Information Search
Yoo, K. H. & Gretzel, U. (2008). Use and Impact of Online Travel Reviews. O’Connor, P., Höpken, W. & Gretzel, U. (Eds.). Information and Communication Technologies in Tourism 2008, 35-46. Vienna, Austria: Springer.
Yoo, K. H., & Gretzel, U. (2008). The Influence of Involvement on Use and Impact of Online Travel Reviews. Hospitality Information Technology Association Conference, Austin, TX, June 15-16, 2008.
Gretzel, U. (2009). Das Online-Suchverhalten von Touristen. (in German). Zeitschrift für Tourismuswissenschaft, Special Issue on New Media, 2(1), 151-164.
Xiang, Z., & Gretzel, U. (2010). Role of Social Media in Online Travel Information Search. Tourism Management, 31 (2), 179-188.
Simms, A., & Gretzel, U. (2013). Planning a vacation using social media: Influences of demographic, psychographic, and trip-related characteristics. ENTER Conference 2013. http://ertr.tamu.edu/ files/2013/03/enter2013_submission_15.pdf
Characteristics and Perceptions of CGM
Lee, W., & Gretzel, U. (2007). Impact of Sensory Information on Evaluations of Online Travel Reviews. In Hsu, C. and H. Tsai (Eds.), Proceedings of the 12th Annual Graduate Education and Graduate Student Research Conference in Hospitality and Tourism, Houston, TX, January 4-6, 2007, pp. 815-822.
Yoo, K.-H., & Gretzel, U. (2009). Generational Differences in CGM Perceptions and Use for Travel Planning. In J. Petrick (Ed.), 40th Annual Proceedings of the Travel and Tourism Research Association Conference. Honolulu, HI, June 21-24, 2009. Travel and Tourism Research Association.
Yoo, K. H., Lee, K. S., & Gretzel, U. (2007). The role of Source Characteristics in eWOM: What Makes Online Travel Reviewers Credible and Likeable? In M. Sigala, L. Mich, J. Murphy, and A. Frew (Eds.), Proceedings of the 14th International ENTER Conference in Ljubljana, Slovenia, January 24-26, 2007, pp. 23-34. UK, Axon Imprint.
Yoo, K.-H., & Gretzel, U. (2010). Antecedents and Impacts of Trust in Travel-Related Consumer Generated Media. Journal of Information Technology & Tourism, 12 (2), 139-152.
Yoo, K.-H., Lee, Y.-J., Gretzel, U., & D. R. Fesenmaier (2009). Trust in Travel-Related Consumer Generated Media. In W. Höpken, U. Gretzel & R. Law (Eds.), Information and Communication Technologies in Tourism 2009, pp. 49-60. Vienna, Austria: Springer Verlag.
Maister, T. & Gretzel. U. (2018). What is Branded Content and is it Ethical? The Relevance Report 2019. Los Angeles, CA: USC Annenberg Center for Public Relations.
Yoo, K.-H., & Gretzel, U. (2009). Comparison of Deceptive and Truthful Travel Reviews. In W. Höpken, U. Gretzel & R. Law (Eds.), Information and Communication Technologies in Tourism 2009, pp. 37-48. Vienna, Austria: Springer Verlag.
Gretzel, U. (2022). Online Reviews. In Buhalis, D. (Ed.), Encyclopedia of Tourism Marketing and Management. Northampton, MA: Edward Elgar Publishing.
Yoo, K.-H., & Gretzel, U. (2009). Detection of Deceptive Hotel Reviews: Influences of Length and Type of Review. Proceedings of the 14th Annual Graduate Student Research Conference in Hospitality and Tourism. Las Vegas, January 4-6, 2009.
Social Media as Communication
As a tourism researcher with a PhD in Communications, looking at social media from a communication perspective is of great importance to me. Three distinct sub-streams of research belong to this theme: 1) social media as a language and rhetorical device; 2) marketing communications using social media; and, 3) communication flows mediated by travel opinion leaders and influencers (Table 4). I have adopted a linguistics lens to examine the peculiarities of social media language, such as emojis and hashtags. More recently, I have followed the visual turn in social media, with images and videos increasingly replacing text (Ge & Gretzel, 2019). In addition, I have looked at social media contents using rhetorical theory to understand argumentation and persuasion in social media contexts. Humor embedded in posts and memes plays a crucial role in grabbing the attention of social media users and eliciting engagement in the forms of likes, comments, or shares.
How to effectively market tourism services and destinations using social media is an issue with which many tourism marketers continue to struggle. Conceptualizing social media marketing communications as conversations and value co-creation opportunities that require unique approaches and extensive organizational commitment has been my focus in this research stream. Opinion leaders and influencers who translate the vast amount of available travel information into bite-sized, entertaining, and relevant contents for their loyal followers are increasingly mediating communication flows between marketers and consumers. I have been following this phenomenon for over a decade now, starting with key opinion leaders in China. Understanding the role of these influencers in destination marketing is a central theme in my current work (see Femenia-Serra & Gretzel, 2022).
Table 4. Social Media as Communication.
Linguistic and Rhetorical Perspectives
De Ascaniis, S. & Gretzel, U. (2012). What’s in a Travel Review? In Fuchs, M., Ricci, F., and Cantoni, L. (Eds.), Information and Communication Technologies in Tourism 2012, pp. 494-505. Vienna, Austria: Springer.
Ge, J. & Gretzel, U. (2017). The Role of Humour in Driving Customer Engagement. In Schegg, R. & Stangl, B. (Eds.). Information and Communication Technologies in Tourism 2017, pp. 461-474. Cham, Switzerland: Springer International.
De Ascaniis, S. & Gretzel, U. (2013). Communicative functions of Online Travel Review titles. A pragmatic and linguistic investigation of destination and attraction OTR titles. Studies in Communication Sciences, 13(2), 156-165.
Ge, J., Gretzel, U. & Zhu, Y. (2018). Humour in Firm-initiated Social Media Conversations – A Conceptual Model. International Journal of Digital Culture and Electronic Tourism, 2(4), 273-293.
Gretzel, U. (2015). #justsayin. Poem. CCT Conference, Fayetteville, Arkansas, June 18-21, 2015. Published in Sherry, J. F., Schouten, J., & Downey, H. (Eds.). Chicksaw Craft Threnody, p. 10. South Bend, Indiana: Aire Lyre Media.
Ge, J. & Gretzel, U. (2018). Impact of Humour on Firm-Initiated Social Media Conversations. Journal of Information Technology & Tourism, 18(1-4), 61-83.
Gretzel, U. (2017). The Visual Turn in Social Media Marketing. Tourismos, 12(3), 1-18.
Ge, J. & Gretzel, U. (2019). Social Media-based Visual Strategies in Tourism Marketing. International Journal of Semiotics and Visual Rhetoric, 2(2): 23-40.
Ge, J. & Gretzel, U. (2018). Emoji Rhetoric – A Social Media Influencer Perspective. Journal of Marketing Management, 34(15-16), 1272-1295.
Shao, J., Yi, S., Shen, Y., Gretzel, U. & Joppe, M. (2020). Research on the Influence of Emoji Communication on the Perception of Destination Image: The Case of Finland. In Paris, C. M. & Benjamin, S. (Eds.), Proceedings of the 2020 TTRA International Conference. June 16-18, 2020, Victoria, BC, Canada. Whitehall, MI: Travel and Tourism Research Association. https://scholarworks.umass.edu/ ttra/2020/research_papers/19/
Marketing Communication
Gretzel, U. (2006). Consumer-Generated Content – Trends and Implications for Branding. eReview of Tourism Research, 4 (3).
Yoo, K.-H., & Gretzel, U. (2010). Web 2.0: New Rules for Tourism Marketing, 41st Annual Proceedings of the Travel and Tourism Research Association Conference. San Antonio, TX, June 20-22, 2010. Travel and Tourism Research Association.
Shao, J., Davila, M.A., & Gretzel, U. (2012). Riding the Social Media Wave: Strategies of DMOs who successfully engage in social media marketing. In Sigala, M., Christou, E., & Gretzel, U. (Eds.), Social Media in Travel, Tourism and Hospitality (pp. 87-98). Brookfield, VT: Ashgate.
Gretzel, U. & Yoo, K. H. (2013). Premises and Promises of Social Media Marketing in Tourism. In McCabe, S. (Ed.), The Routledge Handbook of Tourism Marketing, pp. 491-504. New York: Routledge.
Buhalis, D., Mistilis, N., & Gretzel, U. (2014). Future eDestination Marketing: Perspective of an Australian Tourism Stakeholder Network. Journal of Travel Research, 53(6), 778-790.
Tischler, S. & Gretzel, U. (2017). Online-Marketing in Australien und Neuseeland. In Pforr, C. & Reiser, D. (Eds.), Tourismus in Australien und Neuseeland, pp. 79-94. Berlin: DeGruyter.
Ge, J. & Gretzel, U. (2018). A Taxonomy of Value Co-creation on Weibo – A Communication Perspective. International Journal of Contemporary Hospitality Management, 30(4), 2075-2092.
Gretzel, U. (2022). Online Reputation Management. In Buhalis, D. (Ed.), Encyclopedia of Tourism Marketing and Management. Northampton, MA: Edward Elgar Publishing.
Opinion Leadership and Influencers
Yoo, K.-H., Gretzel, U. & Zach, F. (2011). Travel Opinion Leaders and Seekers. In Law, R., Fuchs, M. and Ricci, F. (Eds.), Information and Communication Technologies in Tourism 2011, pp. 525-536. Vienna, Austria: Springer Verlag.
Shao, J., & Gretzel, U. (2011). Social Media Created the Chinese Backpacker Star. In Frost, W., Croy, G., Laing, J., and Beeton, S. (Eds.), International Tourism and Media Conference, 28-29 November. La Trobe University and Monash University: Melbourne.
Hochmeister, M., Gretzel, U., & Werthner, H. (2013). Destination Expertise in Online Travel Communities. In Cantoni, L. & Xiang, Z. (Eds.), Information and Communication Technologies in Tourism 2013, pp. 219-230. Berlin: Springer.
Shao, J. & Gretzel, U. (2014). Integrating Social Media Influencers into the Marketing Strategy of Chinese Travel Communities (Abstract). In Griffin, K. & Joppe, M. (Eds.). Proceedings of the ttra 2014 International Conference, Brugge, Belgium, June 18-20, 1079-1084.
Linton, H., Han, S. & Gretzel, U. (2017). TripAdvisor Super Contributors: Projecting Professionalism. Frontiers in Service Conference, June 22-25, 2017. New York.
Gretzel, U. (2018). Influencer marketing in travel and tourism. In Sigala, M. & Gretzel, U. (Eds.), Advances in Social Media for Travel, Tourism and Hospitality: New Perspectives, Practice and Cases, pp. 147-156. New York: Routledge.
Femenia-Serra, F. & Gretzel, U. (2020). Influencer Marketing for Tourism Destinations: Lessons from a Mature Destination. In Neidhardt, J. & Wörndl, W. (Eds.), Information and Communication Technologies in Tourism 2020, pp. 65-78. Cham, Switzerland: Springer.
Femenia-Serra, F. & Gretzel, U. (2022). Destination Influencer Marketing. In Buhalis, D. (Ed.), Encyclopedia of Tourism Marketing and Management. Northampton, MA: Edward Elgar Publishing.
Social Media as a Form of Sociality
Social media get their name from their ability to connect people, and from the opportunities they provide for users to share content and socialize, i.e., discuss, debate, organize, show off, argue, and commune, online. The social aspects of social media are especially relevant for tourism as an activity that creates and fosters bonds and for which storytelling and information sharing have always been central aspects. In this context, I have looked at identity construction in online communities and among bloggers. Most of my research on online sociality has focused on the fans of TV shows that use social media to organize as a community that often engages in travel. Most recently, I have become interested in the #vanlife community as a neo-tribe with a very strong emphasis on social-media sharing (Gretzel & Hardy, 2019). My research on social media-facilitated sociality has also looked at the relationship between travelers and tourism providers/destinations. It has found that it is a rather complicated one that requires careful management because it is often short-lived and derives from a complex mix of functional and emotional needs. Table 5 provides specific references for the two sub-topics within this lens.
Table 5. Social Media as a Form of Sociality.
Identity Construction, Cyberfandom & Neo-tribes
Scarpino, M., & Gretzel, U. (2008). Cyberfandom: Understanding the new generation of media-induced travelers. In Croy, G., Beeton, S. & Frost W. (Eds.). Proceedings of the International Tourism and Media Conference. Melbourne, Australia: LaTrobe University & Monash University.
Lee, Y., & Gretzel, U. (2014). Cross-cultural Differences in Social Identity Formation through Travel Blogging. Journal of Travel and Tourism Marketing, 31(1), 37-54.
Shao, J., & Gretzel, U. (2009). Online Responses to a Chinese popular TV Series: Implications for Film-Induced tourism. In L. Lowry (Ed.), Proceedings of the 2009 Annual International Society of Travel and Tourism Educators (ISTTE) Conference, October 15-17, 2009 in San Antonio, TX (Vol 21, pp.224-235). St. Clair Shores, MI: ISTTE.
Dinhopl, A., Gretzel, U. & Whelan, A. (2015). Labeling as a Social Practice in Online Consumption Communities. Special Issue on Online Consumption Communities. Psychology & Marketing, 32(3), 240-249.
Lee, Y.-J., Yoo, K.-H., & Gretzel, U. (2009). Social Identity Formation Through Blogging: Comparison of U.S. and Korean Travel Blogs. Proceedings of the 14th Annual Graduate Student Research Conference in Hospitality and Tourism. Las Vegas, January 4-6, 2009.
Shao, J. & Gretzel, U. (2018). Power of Dramas: A Comparison of Voluntourism between Chinese and American Film Tourists. In Kim, S., & Reijnders, S. (Eds.), Film Tourism in Asia, pp. 187-201. Singapore: Springer Nature.
Shao, J., Scarpino, M., Lee, Y., & Gretzel, U. (2012). Media-Induced Voluntourism in Yunnan, China. Tourism Review International, 15(3), 277-292.
Gretzel, U. & Hardy, A. (2019). #VanLife: Materiality, Makeovers and Mobility amongst Digital Nomads. e-Review of Tourism Research, 16(2/3): 1-9.
Relationship with tourism businesses and destinations
Gretzel, U. & Fesenmaier, D. R. (2012). Customer Relations 2.0 – Implications for Destination Marketing. TTRA Annual International Conference, June 17-19, 2012. Virginia Beach, VA. http://scholarworks.umass.edu/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=1755&context=ttra
Gretzel, U. & Dinhopl, A. (2014). Breaking Up is Hard to Do: Why Do Travellers Unlike Travel-Related Organizations? In Xiang, Z. & Tussyadiah, I. (Eds.), Information and Communication Technologies in Tourism 2014, pp.267-280. Berlin: Springer.
Social Media as Experience
Social media can also be viewed from a phenomenological perspective, as an increasingly central part of human experience in everyday life and during travel. Social media impact tourism experiences and create new forms of touristic experiences. Through this lens, I have explored how social media influence the tourist gaze, how they shape experiences before, during and after the trip, and how they change tourism in specific contexts, such as city tourism and adventure travel (Table 6). In relation to the tourist gaze, I have been interested in selfies as a particularly prominent way in which social media impact on touristic practices. In Dinhopl and Gretzel (2018), we show that social media audiences are internalized and guide every detail of the experience, from planning to post-trip social media sharing. My other work has also shown that these impacts span all phases of the experience, from the dreaming phase to trip satisfaction (Sedera et al., 2017) and post-trip memory work.
Table 6. Social Media as Experience.
Social Media-Enabled Tourist Gaze
Gretzel, U. (2010). Travel in the Network: Redirected Gazes, Ubiquitous Connections and New Frontiers. In Levina, M. & Kien, G. (Eds.). Post-global Network and Everyday Life, pp. 41-58. New York: Peter Lang.
Dinhopl, A. & Gretzel, U. (2016). Selfie-taking as touristic looking. Annals of Tourism Research. 57, 126-139.
Dinhopl, A. & Gretzel, U. (2015). Consumer Soiveillance: Observations of the Self by means of New Media Technologies. In Diehl, K. & Yoon, C. (Eds.), Proceedings of the Association of Consumer Research North American Conference, Special session on iMirror/iMirror: Digital Reflections of Self-Consumption. New Orleans, LA, October 1-4, 2015, p. 134.
Kozinets, R., Gretzel, U. & Dinhopl, A. (2017). Self in Art/Self as Art: Museum Selfies as Identity Work. Frontiers in Psychology, 8:731.
Dinhopl, A. & Gretzel, U. (2016). GoPro panopticon: Performing in the surveyed leisure experience, in S. Carnicelli, D. McGillivray, & G. McPherson (Eds.). Digital Leisure Cultures: Critical Perspectives, pp. 66-79. Routledge: London.
Dinhopl, A. & Gretzel, U. (2018). The networked neo-tribal gaze. In Hardy, A., Bennett, A. & Robards, B. (Eds.). Neo-Tribes: Consumption, Leisure and Tourism, pp. 221-234. Cham, Switzerland: Palgrave-Macmillan.
Impact on Experiences Beyond the Trip
Gretzel, U., Fesenmaier, D. R., Lee, Y.-J., & Tussyadiah, I. (2011). Narrating Travel Experiences: The Role of New Media. In R. Sharpley & P. Stone (Eds.), Tourist Experiences: Contemporary Perspectives, pp. 171-182. New York: Routledge.
Sedera, D., Lokuge, S., Atapattu, M., & Gretzel, U. (2017). Likes – the key to my happiness: The moderating effect of social influence on travel experience. Information and Management, 54(6), 825-836.
Gretzel, U. (2021). Dreaming about Travel: A Pinterest Netnography. In Wörndl, W., Koo, C. & Stienmetz, J. (Eds.) Information and Communication Technologies in Tourism 2021, pp.256-268. Cham, Switzerland: Springer.
Specific Experiences
Gretzel, U. (2015). The role of technology-mediation in the context of adventure travel. In Black, R. & Bricker, K. (Eds.), Adventure Programming and Travel for the 21st Century, pp. 451-455. State College, PA: Venture Publishing.
Gretzel, U. (2019). Social Media and the City: Mediated Gazes and Digital Traces. In Šegota, T., Sigala, M., Gretzel, U., Day, J., Kokkranikal, J., Smith, M., Henderson, J. C., Seabra, C., Pearce, P., Davidson, R., Van Zyl, C., Newsome, D., Hardcastle, J., Rakić, T., Future Agendas in Urban Tourism Research: Special Editorial, International Journal of Tourism Cities, 5(2), 109-124. DOI: 10.1108/IJTC-12-2018-0095.
Gretzel, U. (2020). The growing role of social media in city tourism. In Morrison, A. M. & Coca-Stefaniak, J. A. (Eds.). Routledge Handbook of Tourism Cities, pp. 389-399. New York: Routledge.
Social Media as Data
Social media activities lead to digital traces that, when collected for research purposes, become data. This data fuels the algorithms of social media platforms but can also (at least to some extent) be extracted and interpreted to derive research insights and marketing intelligence. While I have used many different kinds of approaches to analyzing social media data, netnography has become my method of choice because it allows me to keep contextual information intact and to derive rich and meaningful insights. Table 7 lists some of my netnography work in tourism that was not included in any of the previous tables.
Doing research on social media and research with social media has sensitized me to specific data quality issues, which are starting to receive attention in the tourism literature (Xiang et al., 2018). For instance, numerical ratings in online travel reviews do not necessarily correspond with the sentiment expressed in the review text (Jiang, Gretzel & Law, 2010). And established approaches like semiotics, which has gained in importance as social media data have become more visual, need to be adjusted to fit the social media context and need to address the ethical considerations necessary for social media research (Ge & Gretzel, 2022).
Table 7. Social Media as Data.
Netnography
Gretzel, U. (2017). #travelselfie: a netnographic study of travel identity communicated via Instagram. In Carson, S. & Pennings, M. (Eds.), Performing Cultural Tourism: Communities, Tourists and Creative Practices, pp. 115-128. New York: Routledge.
Kennedy-Eden, H. & Gretzel, U. (2021). My Heritage in my Pocket: Mobile Device and App Use by Genealogy Tourists. Journal of Information Technology & Tourism, forthcoming.
Gretzel, U. & Murphy, J. (2019). Making Sense of Robots – Consumer Discourse on Robots in Tourism and Hospitality Service Settings. In Ivanov, S. & Webster, C. (Eds.). Robots, Artificial Intelligence and Service Automation in Travel, Tourism and Hospitality, pp. 93-104. Bingley, UK: Emerald Publishing.
Kozinets, R.V. & Gretzel, U. (2022). Netnography. In Buhalis, D. (Ed.), Encyclopedia of Tourism Marketing and Management. Northampton, MA: Edward Elgar Publishing.
Rastegar, R., Zarezadeh., Z. & Gretzel, U. (2021). World Heritage and Social Justice: Insights from the Inscription of Yazd, Iran. Journal of Sustainable Tourism, 29(2/3), 520-539.
Social Media Data & Analysis
Jiang, J., Gretzel, U., & Law, R. (2010). Do Negative Experiences Always Lead to Dissatisfaction? – Testing Attribution Theory in the Context of Online Travel Reviews. In Gretzel, U., Law, R. and M. Fuchs (Eds.), Information and Communication Technologies in Tourism 2010, pp. 297-308. Vienna, Austria: Springer Verlag.
Ge, J., Alonso Vazquez, M. & Gretzel, U. (2018). Sentiment analysis: a review. In Sigala, M. & Gretzel, U. (Eds.), Advances in Social Media for Travel, Tourism and Hospitality: New Perspectives, Practice and Cases, pp. 243-261. New York: Routledge.
Ge, J. & Gretzel, U. (2022). Social Media Semiotics. In Buhalis, D. (Ed.), Encyclopedia of Tourism Marketing and Management. Northampton, MA: Edward Elgar Publishing.
Marketing Intelligence
Gretzel, U., Lee, W. & K.S. Lee (2006). Listening to the Stories Consumers Tell. Proceedings of the Korea e-Tourism Forum. Seoul, Korea, September 8-9, 2006.
Jiang, J., Gretzel, U. & Law, R. (2014). Influence of Star Rating and Ownership Structure on Brand Image of Mainland China Hotels. Journal of China Tourism Research, 10(1), 69-94.
The Future of Social Media Research
Reflecting on my social media-related research journey fills me with gratitude to all my wonderful collaborators and co-authors. Very often it was them who charted the paths forward and it was their passion that inspired me. Thinking about the different themes that I have explored with them also makes me feel antsy because it is pretty clear that there is so much more that warrants investigation. Given the dynamic nature of social media, I realize that many themes remain underexplored and that many of the topics should be re-investigated as social media technologies and use cultures continue to evolve. Thus, while it is nice to summarize my research in this area and emphasize my contributions, I see the greatest value of this exercise in providing a research framework that illustrates different ways of understanding social media and, thus, can help with identifying research priorities and gaps.
I often get asked about the future of particular platforms or types of CGM. My answer is always that social media will continue to take on new forms and will transform our lives in ways that we cannot yet anticipate. But I also add that one thing is for certain: they are here to stay and will continue to shape tourism in wonderful as well as disruptive ways. Thus, there will be no shortage of social media-related research topics in the future.
Written by Ulrike Gretzel, University of Southern California, USA
Read Ulrike’s letter to future generations of tourism researchers
References
Dinhopl, A. & Gretzel, U. (2016). Conceptualizing tourist videography. Information Technology & Tourism, 15(4), 395-410.
Dinhopl, A. & Gretzel, U. (2018). The networked neo-tribal gaze. In Hardy, A., Bennett, A. & Robards, B. (Eds.). Neo-Tribes: Consumption, Leisure and Tourism, pp. 221-234. Cham, Switzerland: Palgrave-Macmillan.
Femenia-Serra, F. & Gretzel, U. (2022). Destination Influencer Marketing. In Buhalis, D. (Ed.), Encyclopedia of Tourism Marketing and Management. Northampton, MA: Edward Elgar Publishing.
Finkel, E. J., Eastwick, P. W., Karney, B. R., Reis, H. T., & Sprecher, S. (2012). Online dating: A critical analysis from the perspective of psychological science. Psychological Science in the Public Interest, 13(1), 3-66.
Ge, J. & Gretzel, U. (2019). Social Media-based Visual Strategies in Tourism Marketing. International Journal of Semiotics and Visual Rhetoric, 2(2): 23-40.
Ge, J. & Gretzel, U. (2022). Social Media Semiotics. In Buhalis, D. (Ed.), Encyclopedia of Tourism Marketing and Management. Northampton, MA: Edward Elgar Publishing.
Gretzel, U. (2017). Social Media Activism in Tourism. Journal of Hospitality and Tourism, 15(2), 1-14.
Gretzel, U. (2018). Tourism and Social Media. In Cooper, C., Gartner, W., Scott, N. & Volo, S. (Eds.). The Sage Handbook of Tourism Management, Volume 2, pp. 415-432. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.
Gretzel, U. (2019). The Role of Social Media in Creating and Addressing Overtourism. In Dodds, R. & Butler, R. (Eds.). Overtourism: Issues, realities and solutions, pp. 62-75. Berlin: De Gruyter.
Gretzel, U. & Hardy, A. (2019). #VanLife: Materiality, Makeovers and Mobility amongst Digital Nomads. e-Review of Tourism Research, 16(2/3): 1-9.
Gretzel, U., Lee, W. & Lee, K.S. (2006). Listening to the Stories Consumers Tell. Korea e-Tourism Forum. Seoul, Korea, September 8-9, 2006.
Gretzel, U., Yoo, K. H. & M. Purifoy (2007). Online Travel Reviews Study. Technical Report. College Station, TX: Laboratory for Intelligent Systems in Tourism. Accessed online at (August 1, 2021): https://www.tripadvisor.com/pdfs/OnlineTravelReviewReport.pdf.
Isacsson, A. & Gretzel, U. (2011). Facebook as an edutainment medium to engage students in sustainability and tourism. Journal of Hospitality and Tourism Technology, 2(1), 81-90.
Jiang, J., Gretzel, U., & Law, R. (2010). Do Negative Experiences Always Lead to Dissatisfaction? – Testing Attribution Theory in the Context of Online Travel Reviews. In Gretzel, U., Law, R. and M. Fuchs (Eds.), Information and Communication Technologies in Tourism 2010, pp. 297-308. Vienna, Austria: Springer Verlag.
Kozinets, R. V. (2020). Netnography: The essential guide to qualitative social media research. London: Sage.
Kozinets, R., Patterson, A., & Ashman, R. (2017). Networks of desire: How technology increases our passion to consume. Journal of Consumer Research, 43(5), 659-682.
Pratt, S., & Tolkach, D. (2020). Stupidity in tourism. Tourism Recreation Research, https://doi.org/10.1080/02508281.2020.1828555.
Mariani, M. M., Borghi, M., & Gretzel, U. (2019). Online reviews: Differences by submission device. Tourism Management, 70, 295-298.
Sedera, D., Lokuge, S., Atapattu, M., & Gretzel, U. (2017). Likes – the key to my happiness: The moderating effect of social influence on travel experience. Information and Management, 54(6), 825-836.
Vargo, S. L., Maglio, P. P., & Akaka, M. A. (2008). On value and value co-creation: A service systems and service logic perspective. European Management Journal, 26(3), 145-152.
Xiang, Z., Du, Q., Ma, Y., & Fan, W. (2018). Assessing reliability of social media data: lessons from mining TripAdvisor hotel reviews. Information Technology & Tourism, 18(1), 43-59.
Xiang, Z. & Gretzel, U. (2010). Role of Social Media in Online Travel Information Search. Tourism Management, 31 (2), 179-188.
Zarezadeh, Z., Rastegar, R. & Gretzel, U. (2018). Reviewing the Past to Inform the Future: A Literature Review of Social Media in Tourism. Czech Journal of Tourism, 7(2), 115-131.
Zhou, L., Zhang, P., & Zimmermann, H. D. (2013). Social commerce research: An integrated view. Electronic commerce research and applications, 12(2), 61-68.

